
Indus Valley Civilization MCQs for UPSC Archives THE LIVE LEARNS
Az Indus-völgyi civilizáció vagy Harappan civilizáció, amely az ősi Harappa városáról kapta a nevét, egy bronzkori civilizáció, amelynek területe az Indus folyó völgye körül húzódott a nyugat-indiai szubkontinensen (a mai Pakisztán és környéke). Az úgynevezett „érett" korszaka körülbelül i. e. 2600-tól i. e.
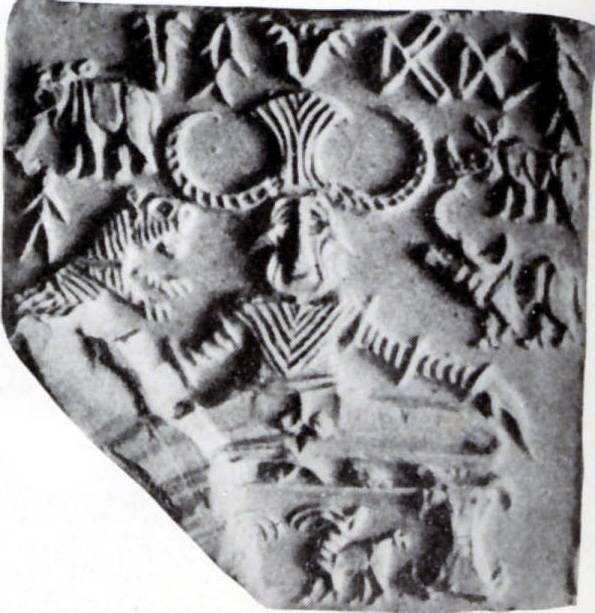

Indusvölgyi pecsételők
Az Indus folyó nagyrészt a mai Pakisztán területén folyik, erről nevezték el ezt a civilizációt Indus-völgyinek. Indus-völgyi civilizáció Arra is van példa, hogy úgy említik, mint Harappa-civilizáció, mivel azon a helyen találtak először bizonyítékot ennek a számottevő kultúrának a létezésére.

Az Indusvölgyi civilizáció még annál is öregebb, mint gondoltuk 24.hu
Indus Valley Civilisation. Excavated ruins of Mohenjo-daro, Sindh province, Pakistan, showing the Great Bath in the foreground. Mohenjo-daro, on the right bank of the Indus River, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site, the first site in South Asia to be so declared. Miniature votive images or toy models from Harappa, c. 2500 BCE.
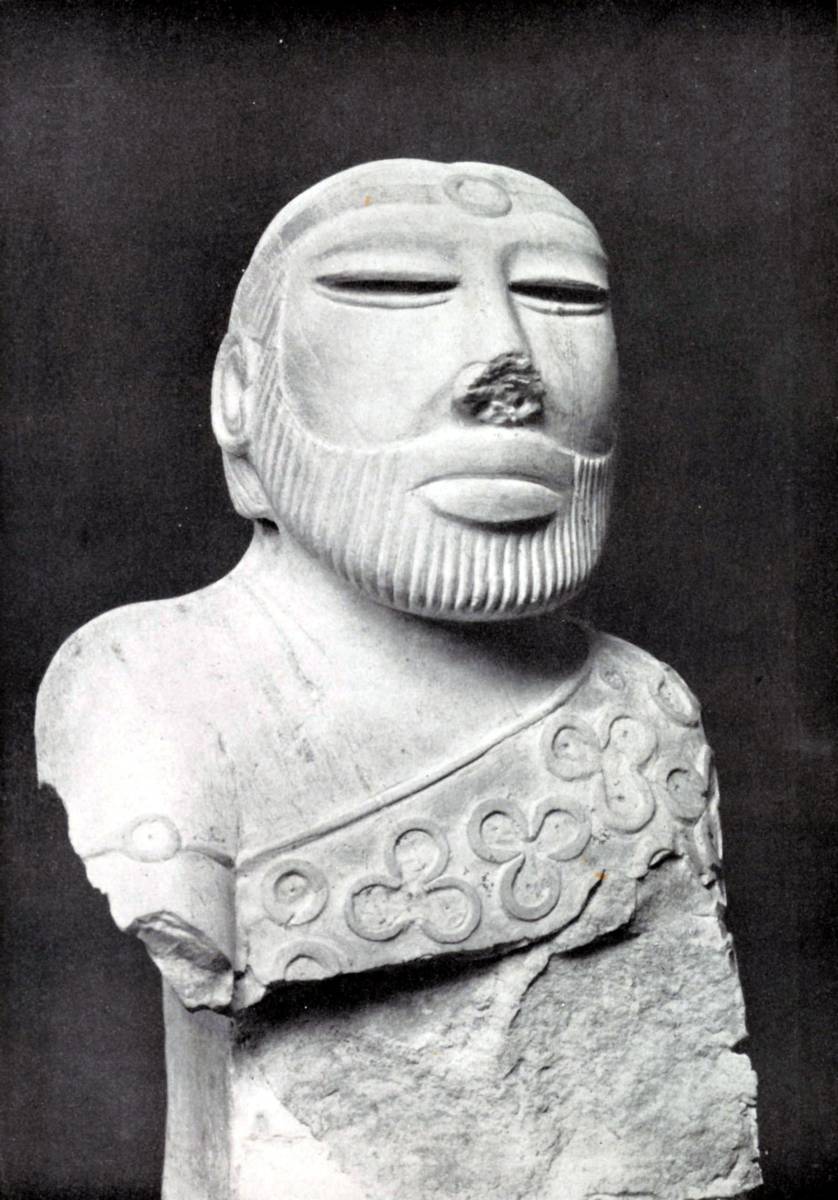

Az Indusvölgyi civilizáció szobrászata
The Indus civilization peaked around 2500 B.C.E. in the western part of South Asia. Geographically, it was spread over an area of some 1,250,000 km², comprising the whole of modern-day Pakistan and parts of modern-day India and Afghanistan. The Indus civilization is among the world's earliest civilizations, contemporary to the great Bronze Age.
Indus Valley Architecture
India - Indus Valley, Harappan, Bronze Age: While the Indus (or Harappan) civilization may be considered the culmination of a long process indigenous to the Indus valley, a number of parallels exist between developments on the Indus River and the rise of civilization in Mesopotamia. It is striking to compare the Indus with this better-known and more fully documented region and to see how.

Pin de Edit Szakács en IndusVölgyi civilizáció Arte negro, Arte
The Indus Valley Civilization is one of the oldest civilizations in human history. It arose on the Indian subcontinent nearly 5,000 years ago — roughly the same time as the emergence of ancient.

Cities of the Indus Valley Linking to Thinking
The Indus Valley Civilization was a cultural and political entity which flourished in the northern region of the Indian subcontinent between c. 7000 - c. 600 BCE. Its modern name derives from its location in the valley of the Indus River, but it is also commonly referred to as the Indus-Sarasvati Civilization and the Harrapan Civilization.These latter designations come from the Sarasvati River.
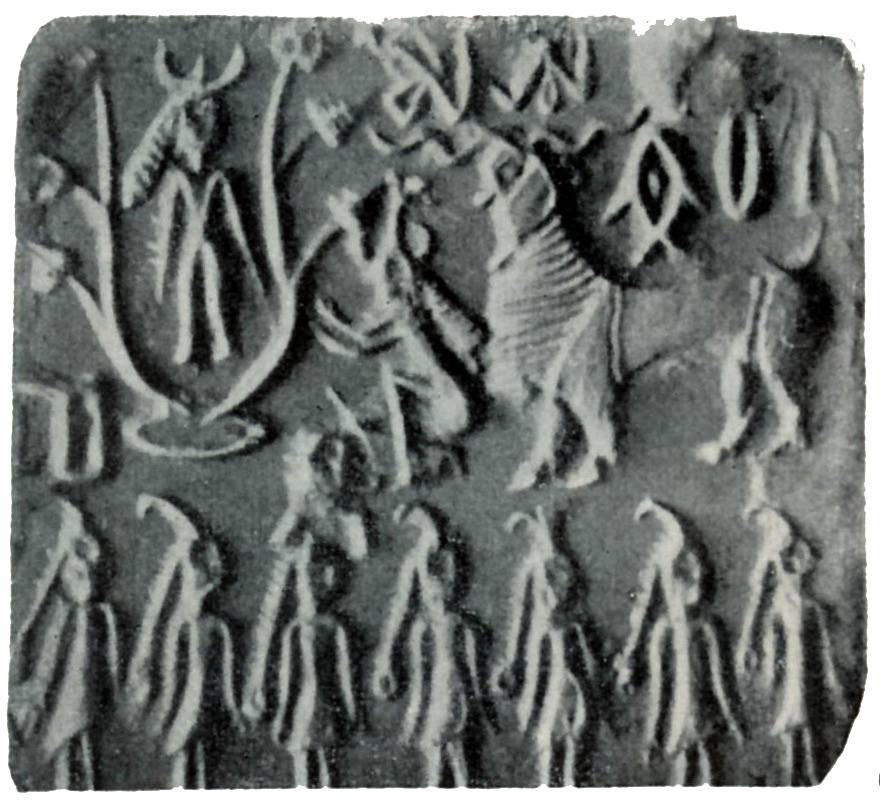

Indusvölgyi pecsételők
Tantárgy/kurzus: Világtörténelem > 1. témakör. 6. lecke: Az ókori India. Az Indus-völgyi civilizáció. Az Indus-völgyi civilizáció. Az Indus-völgyi civilizáció. A védikus kor. A szanszkrit és az angol nyelv rokonsága. A hinduizmus főbb fogalmai: a brahman, az átman, a szamszára és a móksa. Az ókori India.

Adria Tours Indusvölgyi kolostoroktól, Kőrösi Csoma Sándor szobájáig India
A civilizáció stratégiai elhelyezkedése a fő kereskedelmi útvonalak mentén. lehetővé tette , hogy hosszú távú kereskedelemben vegyenek részt, és gazdasági kapcsolatokat. alakítsanak ki a szomszédos társadalmakkal. Az Indus-völgyi emberek képzett kereskedők voltak, és különféle árukat cseréltek, köztük.

Történelem 9. I. AZ ŐSKOR ÉS AZ ÓKORI KELET 6. Az ókori India és Kína
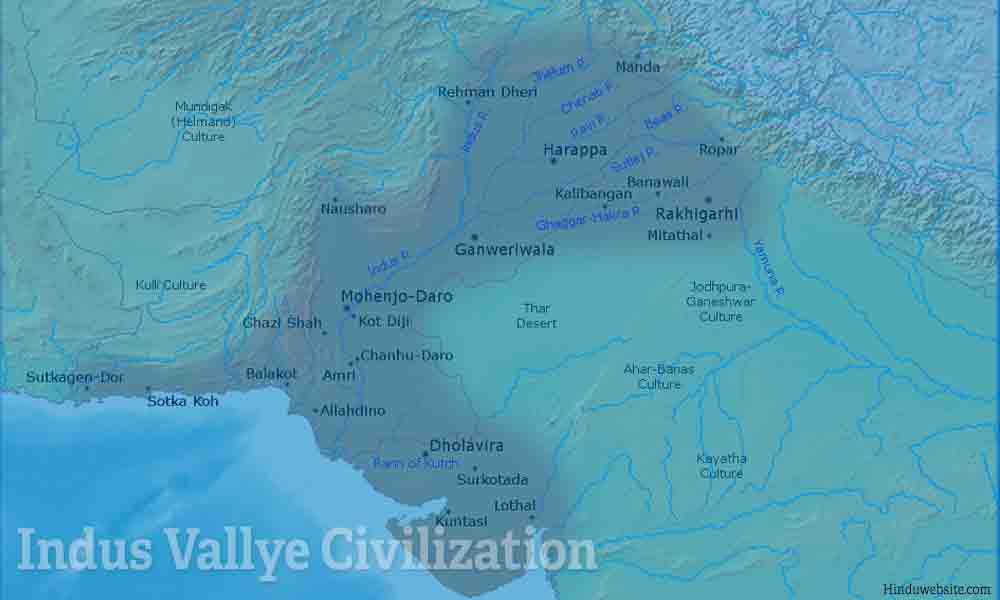
Overview. The Indus River Valley Civilization, 3300-1300 BCE, also known as the Harappan Civilization, extended from modern-day northeast Afghanistan to Pakistan and northwest India. Important innovations of this civilization include standardized weights and measures, seal carving, and metallurgy with copper, bronze, lead, and tin.

279 best IndusVölgyi civilizáció images on Pinterest Harappan, Ancient art and Mohenjo daro
Az Indus-völgyi civilizáció városainak maradványai figyelemre méltó szervezettséget mutatnak; voltak jól kialakított szennyvízelvezető és szemétgyűjtő rendszerek, sőt valószínűleg voltak közfürdők és magtárak is a gabona őrzésére. A legtöbb városlakó kézműves vagy kereskedő volt, akik különálló negyedekben csoportosultak.

Assignment Indus Valley Civilization
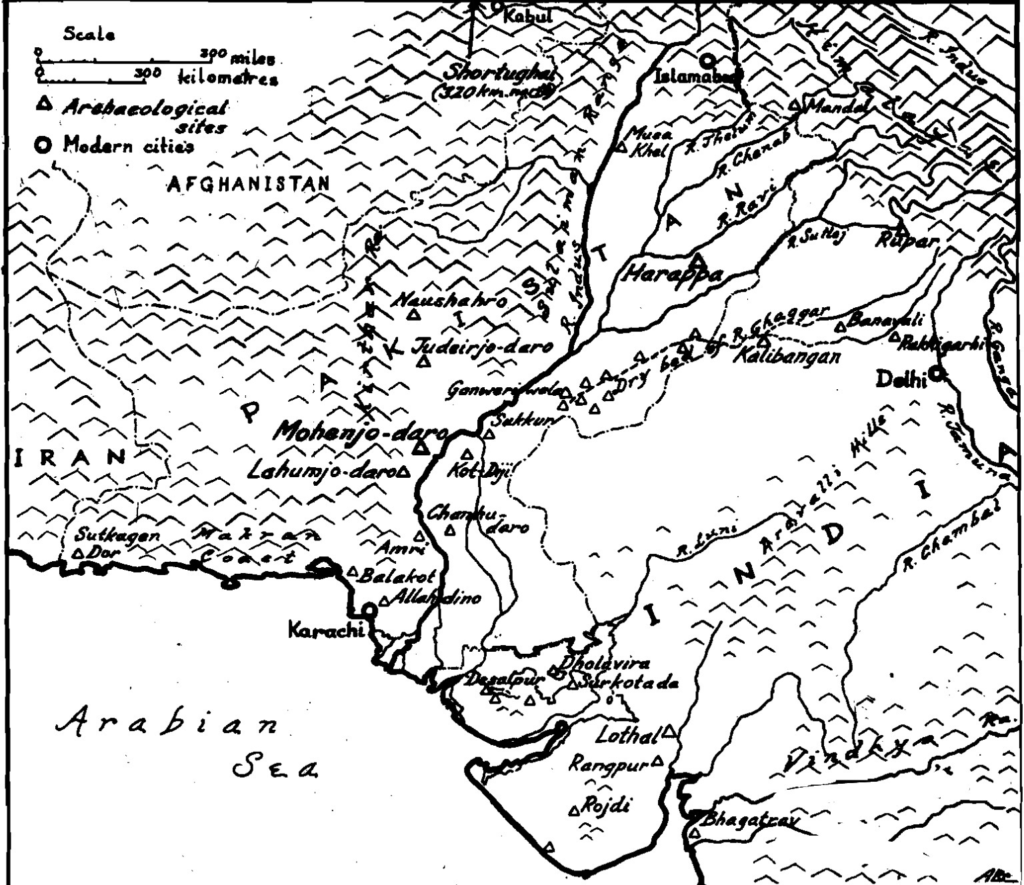
Az Indus-völgyi kultúrák és főbb települések Kr. e. 1900-1300 között. Az Indus-völgyi civilizáció történetéről nem állnak rendelkezésre írásos források. A régészeti leletek tanúsága szerint az i. e. 4. évezred folyamán az őslakosság településein megjelentek a nyugati és déli irányból érkező bevándorlók.

Civilizations of the Indus Valley and Beyond Harappa
Az Indus-völgyi civilizáció az indiai szubkontinens északnyugati részén elterülő bronzkori civilizáció volt Kr. e. 3300-tól Kr. e. 1300-ig; kifejlett formájában pedig Kr. e. 2600-tól kezdve. Az ókori Egyiptommal és Mezopotámiával együtt egyike volt a közel-keleti és dél-ázsiai három korai civilizációnak, és a három közül kb. 1,25 millió km²-rel a legkiterjedtebb.
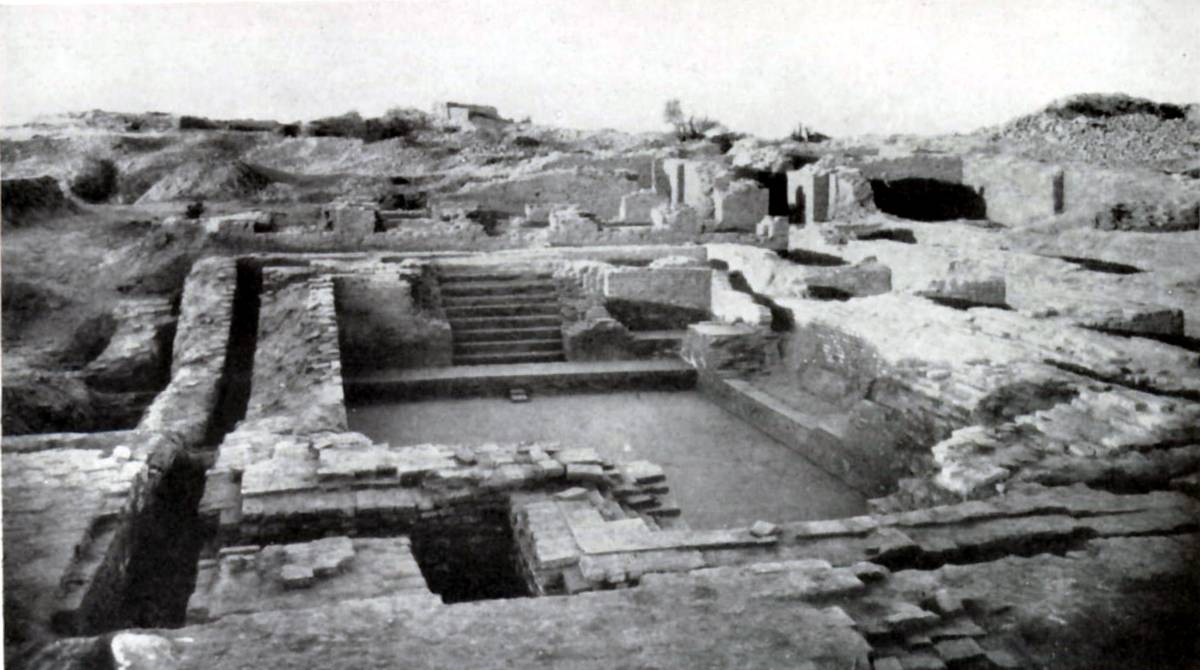

Az Indusvölgyi civilizáció építészete
Indus civilization, the earliest known urban culture of the Indian subcontinent. The nuclear dates of the civilization appear to be about 2500-1700 bce, though the southern sites may have lasted later into the 2nd millennium bce. Among the world's three earliest civilizations—the other two are those of Mesopotamia and Egypt —the Indus.
.png)
Indus Valley Civilisation Wikiwand
The Indus Valley Civilization, (mature period 2600-1900 BCE), abbreviated IVC, was an Bronze Age civilization that flourished in the Indus River basin.It was centred mostly in the western part of the Indian Subcontinent and flourished around the Indus river basin. Primarily centered along the Indus and the Punjab region, the civilization extended into the en:Ghaggar-Hakra River valley and.
The Religion of the Indus Valley Civilization
The Indus Valley Civilization existed through its early years of 3300-1300 BCE, and its mature period of 2600-1900 BCE. The area of this civilization extended along the Indus River from what today is northeast Afghanistan, into Pakistan and northwest India. The Indus Civilization was the most widespread of the three early civilizations of the.